Decoding Algorithmic Trading Essentials

Introduction
Algorithmic trading, often called algo trading, utilizes complex mathematical algorithms and high-speed computing to make trading decisions. Gone are the days of manual trading; today, algorithms execute trades at lightning speed, empowering traders to capitalize on even the slightest market price inefficiencies. Whether you're a seasoned trader or new to the game, understanding the fundamentals of algorithmic trading is essential for success in today's fast-paced markets.
Understanding the fundamentals of algorithmic trading is crucial for any trader looking to stay competitive and profitable in today's markets. By grasping the basics of algorithms, traders can gain insight into market dynamics, identify trading opportunities, and mitigate risks effectively. Whether you're a day trader, swing trader, or long-term investor, having a solid understanding of algo trading fundamentals can help you confidently navigate the complexities of the stock market. So, let's dive into the fundamentals of algorithmic trading and unlock the secrets to success in modern finance.
How Algorithmic Trading Works
In algo trading, algorithms play a central role in making trading decisions. These algorithms are developed using mathematical formulas and historical market data to identify price patterns, trends, and signals that indicate potential trading opportunities. Upon generating a trading signal, the algorithm executes the trade automatically according to predefined parameters like price, quantity, and timing. By removing human emotions from trading, algorithmic trading aims to make trading decisions based on logic, data, and probabilities rather than gut feelings or intuition.
Technology is the backbone of algo trading, enabling traders to execute orders quickly and precisely. High-speed computers, sophisticated algorithms, and low-latency trading infrastructure are essential for algorithmic trading systems. These technologies allow traders to process vast amounts of market data in real time, execute trades within milliseconds, and react to market movements instantaneously. Furthermore, advancements in cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and machine learning have greatly improved the abilities of algorithmic trading systems, paving the way for more sophisticated and adaptive trading strategies.
Understanding market dynamics is critical for success in algo trading. A complicated interplay of supply and demand, investor sentiment, economic indicators, geopolitical events, and other factors drives markets. Algorithmic traders must analyze market data, identify trends and patterns, and adapt their strategies accordingly to capitalize on changing market conditions. Moreover, algo trading can influence market dynamics by amplifying price movements, increasing trading volumes, and shaping market microstructure. By staying attuned to market dynamics and continuously refining their trading algorithms, algorithmic traders have the potential to gain a competitive advantage and achieve consistent profitability in the ever-evolving financial markets.
Key Components of Algorithmic Trading
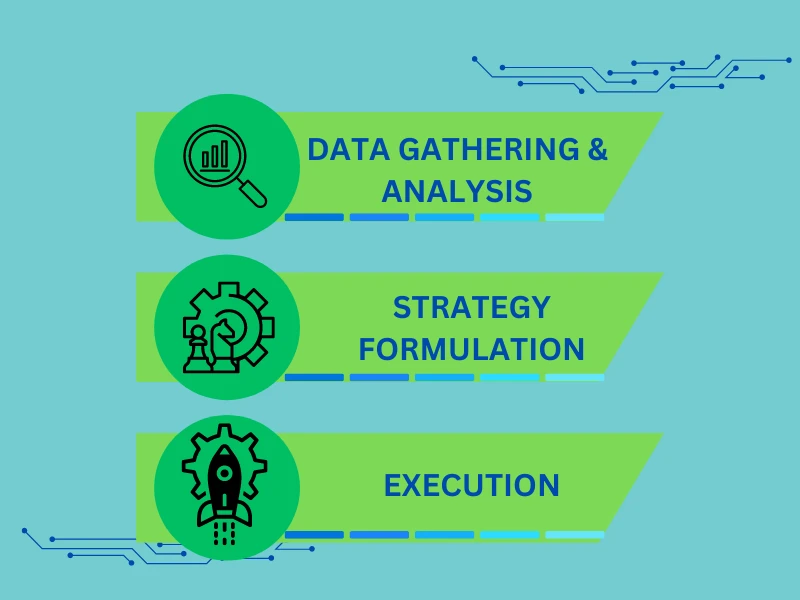
1. Data Gathering and Analysis
Data gathering and analysis are fundamental components of algo trading. Traders use various market data sources, including historical price data, real-time market feeds, economic indicators, and news sentiment, to inform their trading decisions. Accessing accurate and timely data is crucial for identifying trading opportunities, assessing market trends, and making informed decisions. Moreover, data quality plays a vital role in the success of algorithmic trading strategies. Clean, reliable data ensures that algorithms can generate accurate signals and execute trades with confidence, minimizing the risk of errors and false signals.
2. Strategy Formulation
Strategy formulation is developing trading algorithms that define how trades will be executed based on specific criteria and rules. Traders use various techniques and methodologies to formulate trading strategies, ranging from technical analysis and quantitative modeling to machine learning and artificial intelligence. Developing robust trading algorithms requires careful consideration of market conditions, risk tolerance, and trading objectives. Additionally, traders must conduct thorough backtesting and optimization to ensure their algorithms are effective and reliable across different market environments.
3. Execution
Execution is the final component of algo trading, where trades are executed in the market according to predefined parameters and criteria. Order placement is a critical aspect of execution, as it involves determining the optimal price, quantity, and timing for executing trades. Traders use sophisticated algorithms to place orders efficiently and minimize market impact, ensuring that trades are executed at the most favorable prices. Once trades are placed, traders must monitor their positions closely and adjust as needed to adapt to changing market conditions. This may involve modifying trading parameters, adjusting risk levels, or closing out positions to lock in profits or limit losses. Effective execution is essential for maximizing trading performance and achieving consistent profitability in algorithmic trading.
Benefits of Algo Trading
1. Efficiency and Speed
Algo trading offers unparalleled efficiency and speed compared to traditional manual trading methods. With algorithms executing trades automatically based on predefined criteria, trades can be executed within milliseconds, allowing traders to capitalize on fleeting market opportunities that human traders may miss. This speed advantage is especially crucial in today's fast-paced markets, where prices can change rapidly, and split-second decisions can significantly affect profitability.
2. Real-time Execution
One of the critical benefits of algorithmic trading is its ability to execute trades in real time. Unlike human traders, who may delay or miss trade opportunities due to emotional hesitation or indecision, algorithms can execute trades instantaneously as soon as predefined conditions are met. This real-time execution capability ensures that traders can enter and exit positions at the most suitable points, maximizing profit potential and minimizing the impact of market fluctuations.
3. Reduced Human Error
Human error is a common pitfall in manual trading, often leading to costly mistakes such as entering incorrect trade orders or miscalculating risk exposure. Algo trading helps mitigate these risks by automating the trading process and removing the potential for human error. By following pre-programmed rules and algorithms, algorithmic trading systems can execute trades with precision and accuracy, reducing the chances of making costly errors that can negatively impact trading performance.
4. Enhanced Accuracy and Consistency
Algo trading offers enhanced accuracy and consistency in executing trading strategies. Unlike human traders, who may experience fluctuations in performance due to emotional biases or cognitive biases, algorithms operate based on logic and predefined rules. This consistency ensures that trading decisions are made objectively and without the influence of emotions, leading to more reliable and predictable outcomes over time. By adhering strictly to predefined parameters, algorithmic trading systems can maintain a disciplined approach to trading and avoid the pitfalls of impulsive decision-making.
5. Removing Emotional Biases
Emotions such as fear, greed, and excitement can cloud judgment and lead to mindless decision-making in the financial markets. Algo trading helps remove emotional biases from the trading process by executing trades based on predetermined criteria without human intervention. This removes the emotional rollercoaster often associated with manual trading, allowing traders to approach the market with a clear and rational mindset. By eliminating emotional biases, algorithmic trading systems can make more objective and disciplined trading decisions, improving performance and better risk management.
6. Systematic Approach
Algo trading enables traders to adopt a systematic approach to trading by codifying their trading strategies into algorithms. These algorithms are designed to follow rules and criteria, ensuring disciplined trade execution consistently. This systematic approach helps traders remove the guesswork from their trading decisions and provides a structured framework for evaluating market opportunities. By following predefined rules and protocols, algorithmic trading systems can help traders focus on their trading objectives and avoid impulsive or irrational behavior.
7. Access to Diverse Strategies
Algorithmic trading provides traders access to a wide range of trading strategies that may not be feasible to execute manually. Whether scalping, trend following, statistical arbitrage, or high-frequency trading, algorithms can be tailored to implement various trading strategies with precision and efficiency. This access to diverse strategies allows traders to explore different approaches to the market and diversify their trading portfolio, increasing the potential for profit and reducing overall risk exposure. Furthermore, algo trading systems can simultaneously execute multiple strategies across different asset classes and markets, providing traders unparalleled flexibility and opportunities for portfolio optimization.
8. Scalping, Trend Following, and More
Among the many trading strategies available through algo trading, scalping and trend following are two popular approaches traders use to capitalize on short-term price movements and long-term market trends. Scalping involves making small profits from frequent trades executed within seconds or minutes, exploiting minor price fluctuations in the market. On the other hand, trend following aims to capture more significant profits by riding major market trends and staying invested in the direction of the trend for an extended period. Algorithmic trading systems can implement these strategies with precision, allowing traders to profit from both short-term volatility and long-term market trends.
9. Customization Options
A key benefit of algorithmic trading lies in its customization options, empowering traders to tailor their strategies to their unique preferences and objectives. Whether it's adjusting risk parameters, optimizing entry and exit criteria, or incorporating proprietary indicators, algo trading systems can be customized to accommodate the distinct requirements of individual traders. This level of customization empowers traders to fine-tune their strategies based on market conditions, risk tolerance, and trading goals, giving them greater control over their trading activities. Additionally, algorithmic trading platforms often offer various tools and functionalities that enable traders to test and refine their strategies through backtesting and optimization, ensuring they are adequately equipped to navigate the complexities of the financial markets.
Disadvantages of Algo Trading
1. Complexity and Learning Curve
Algorithmic trading requires a deep understanding of programming languages, statistical analysis, and financial markets, which can pose a significant learning curve for traders. Developing and implementing trading algorithms involves complex processes such as data analysis, strategy formulation, and optimization, which may be challenging for those without a background in quantitative finance or computer science. Moreover, staying updated with the latest technologies and market developments requires continuous learning and adaptation, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
2. Technology Risks
Algo trading relies heavily on technology infrastructure and systems, making it vulnerable to various technology-related risks. Technical glitches, system failures, and connectivity issues can disrupt trading operations and lead to significant financial losses. Moreover, cyber threats such as hacking, malware, and data breaches pose a constant risk to algorithmic trading systems, compromising the integrity and security of trading operations. Traders must invest in robust technology solutions and risk management practices to mitigate these technology risks effectively.
3. Market Complexity and Uncertainty
Financial markets are inherently complex and unpredictable, posing challenges for algorithmic trading strategies. Market dynamics can change rapidly due to factors such as economic indicators, geopolitical events, and investor sentiment, making it difficult for algorithms to adapt quickly and accurately. Moreover, algo trading strategies may inadvertently contribute to market volatility and instability, exacerbating price fluctuations and amplifying systemic risks. Traders must closely monitor market conditions and adjust their algorithms accordingly to navigate the complexities and uncertainties of the financial markets.
4. Overfitting and Data Snooping
Overfitting occurs when a trading algorithm is excessively tailored to historical data, capturing noise rather than actual market patterns. It can lead to misleading backtest results and inflated performance metrics, as the algorithm may perform well in historical data but fail to generalize to future market conditions. Similarly, data snooping refers to the tendency to cherry-pick data or parameters that yield favorable results, leading to overly optimistic expectations about the performance of trading strategies. Traders must avoid overfitting and data snooping by conducting robust out-of-sample testing and using realistic assumptions in their backtesting processes.
5. Liquidity and Market Impact
Algo trading can contribute to liquidity fragmentation and exacerbate market impact, particularly in highly liquid markets where large volumes of trades are executed rapidly. High-frequency trading strategies, in particular, may exacerbate price fluctuations and lead to adverse selection for other market participants. Moreover, algorithmic traders may face challenges in executing large orders without moving the market, as their trading activity can be detected by other participants who may adjust their strategies accordingly. Traders must carefully consider liquidity constraints and market impact when designing and executing algorithmic trading strategies to minimize adverse effects on market quality.
6. Regulatory and Compliance Risks
Algorithmic trading is subject to a complex regulatory landscape, with rules and regulations governing aspects such as order types, market manipulation, and risk controls. Traders must ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, such as pre-trade risk checks, circuit breakers, and reporting obligations, to avoid regulatory scrutiny and potential penalties. Moreover, regulatory changes and enforcement actions can impact the profitability and viability of algo trading strategies, requiring traders to stay informed and adapt their practices accordingly.
7. Dependency on Market Conditions
Algorithmic trading strategies are often designed to exploit specific market conditions or patterns, which can limit their effectiveness in different market environments. For example, a trend-following strategy may perform well during solid market trends but needs help in choppy or range-bound markets. Similarly, mean-reversion strategies may excel during periods of market mean-reversion but underperform during strong trending markets. Traders must be aware of the limitations of their algorithms and adjust their strategies accordingly to adapt to changing market conditions. Additionally, sudden shifts in market dynamics or unforeseen events can render algo trading strategies ineffective, highlighting the importance of diversification and risk management.
8. Operational Complexity and Costs
Implementing and maintaining algorithmic trading systems can be operationally complex and costly, requiring significant investments in technology infrastructure, data feeds, and connectivity. Traders must allocate resources for developing, testing, and optimizing trading algorithms and monitoring and managing their performance in real time. Additionally, algo trading systems may incur ongoing costs such as market data subscriptions, software licenses, and infrastructure maintenance fees. Moreover, the competitive nature of algorithmic trading may necessitate continuous innovation and investment in new technologies and strategies to remain competitive, adding to the overall operational complexity and costs associated with algo trading.
9. Ethical and Social Considerations
Algorithmic trading has raised ethical and social concerns about market fairness, transparency, and integrity. High-frequency trading strategies have been criticized for potentially exacerbating market volatility, increasing systemic risk, and undermining investor confidence. Moreover, the use of algo trading in areas such as market-making, order routing, and price discovery has raised questions about market manipulation and front-running. Traders must consider the ethical implications of their trading activities and adhere to fairness, integrity, and transparency principles to maintain market trust and stability. Additionally, regulators and policymakers may introduce measures to address ethical and social concerns related to algorithmic trading, requiring traders to navigate evolving regulatory frameworks and market expectations.
Conclusion
Algo trading platforms have revolutionized traders' participation in financial markets, offering advanced tools and infrastructure for developing, testing, and executing trading strategies. From retail traders to institutional investors, these platforms provide access to many features and functionalities that empower traders to automate their trading activities and optimize their performance.
However, traders need to approach algorithmic trading platforms with caution and diligence. While these platforms offer significant benefits, they also come with risks like technology failures, data breaches, and regulatory compliance challenges. Traders must conduct thorough research, perform due diligence, and adopt robust risk management practices to mitigate these risks effectively.
In conclusion, algo trading platforms can be a powerful tool for traders to achieve their financial goals by capitalizing on market opportunities. By leveraging the capabilities of these platforms intelligently and responsibly, traders can unlock new avenues for success in today's dynamic and competitive financial markets.